EFSA Surveying Stakeholders on Biotechnologies in Microorganisms for Food and Feed

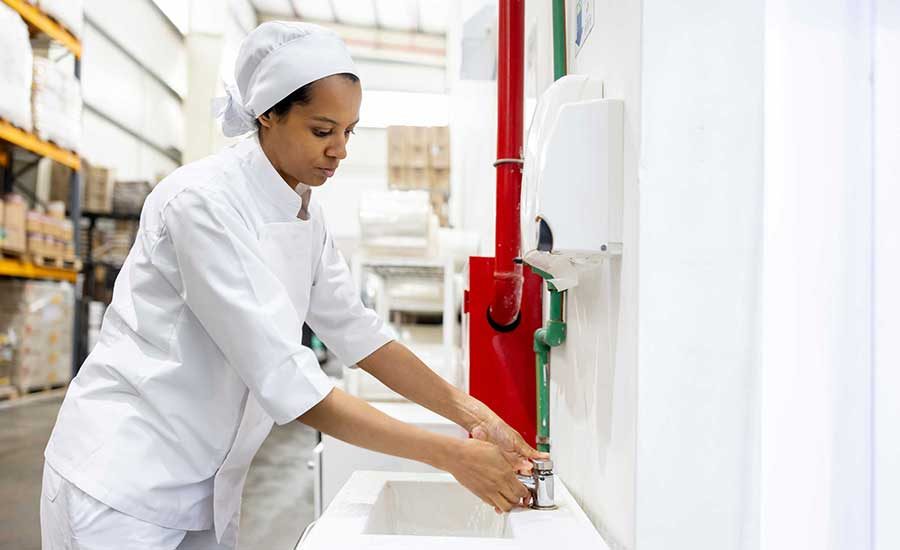
Credit: Yassine Khalfalli via Unsplash
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) is asking interested stakeholders to take a survey about the use of new genomic techniques for the production of genetically modified microorganisms (GMMs) intended for food and feed.
The European Commission requested EFSA to produce an opinion on new developments in biotechnology applied to microorganisms intended for food and feed use in two categories:
- Products derived from GMMs in which GMMs capable of multiplication or of transferring genes are not present, but in which recombinant DNA is still present (e.g., heat-inactivated starter cultures)
- Products consisting of or containing GMMs capable of multiplication or of transferring genes (e.g., live starter cultures for fermented foods and feed).
EFSA will consider data collected through the survey in order to conduct a horizon-scanning exercise on microorganisms and their products obtained by new development in biotechnology, and to form an opinion on potential novel hazards and risks from new developments in biotechnology applied to microorganisms, as well as the adequacy of the current EFSA risk assessment guidance.
New genomic techniques are defined as techniques of genetic manipulation that have emerged or developed after 2001. Examples of NGTs include genome editing techniques, in vivo mutagenesis techniques, and epigenetic techniques. Techniques already in use prior to 2001 that make use of recombinant nucleic acid molecules, also called “established genomic techniques,” are out of scope.
The survey closes April 30, 2023.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!